Co-Attention

So far, all attention models for VQA in literature have focused on the problem of identifying “whereto look” or visual attention. In this paper, we argue that the problem of identifying “which words tolisten to” orquestion attentionis equally important. Consider the questions “how many horses arein this image?” and “how many horses can you see in this image?". They have the same meaning,essentially captured by the first three words.

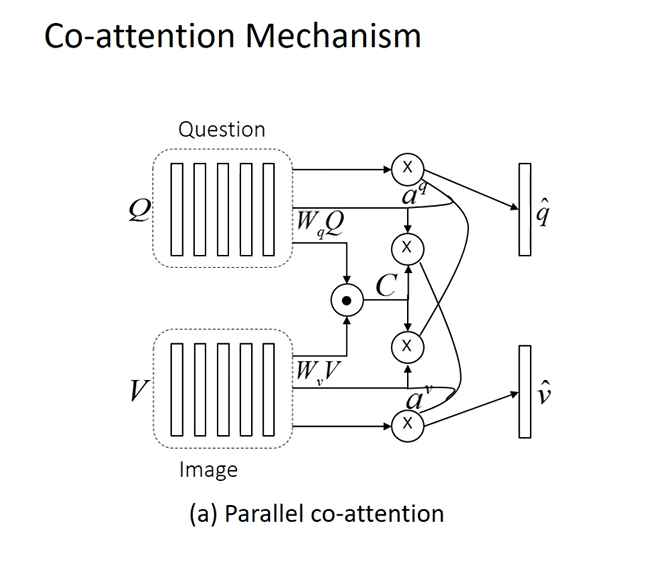
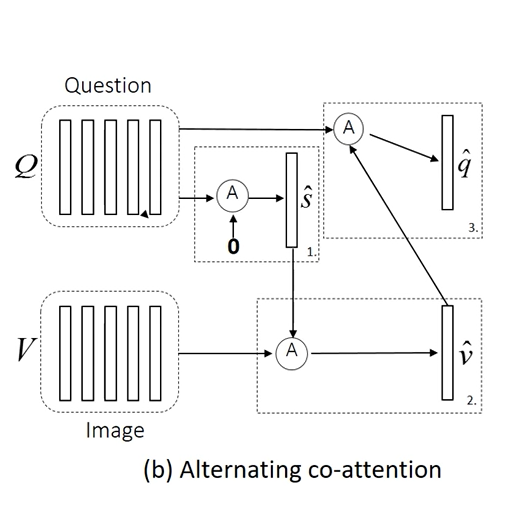
Co-Attention: Paper proposes a novel mechanism that jointly reasons about visual attention and questionattention, which we refer to asco-attention. Unlike previous works, which only focus on visualattention, our model has a natural symmetry between the image and question, in the sense that theimage representation is used to guide the question attention and the question representation(s) areused to guide image attention.
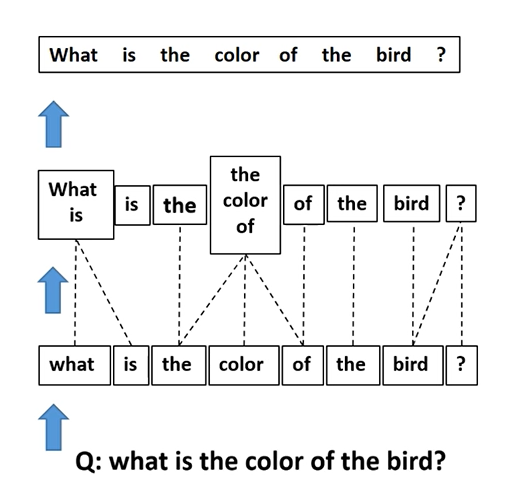
We build a hierarchical architecture that co-attends to the image and questionat three levels:
(a) word level,
(b) phrase level and
(c) question level.
At the word level, we embed thewords to a vector space through an embedding matrix.
At the phrase level, 1-dimensional convolutionneural networks are used to capture the information contained in unigrams, bigrams and trigrams.
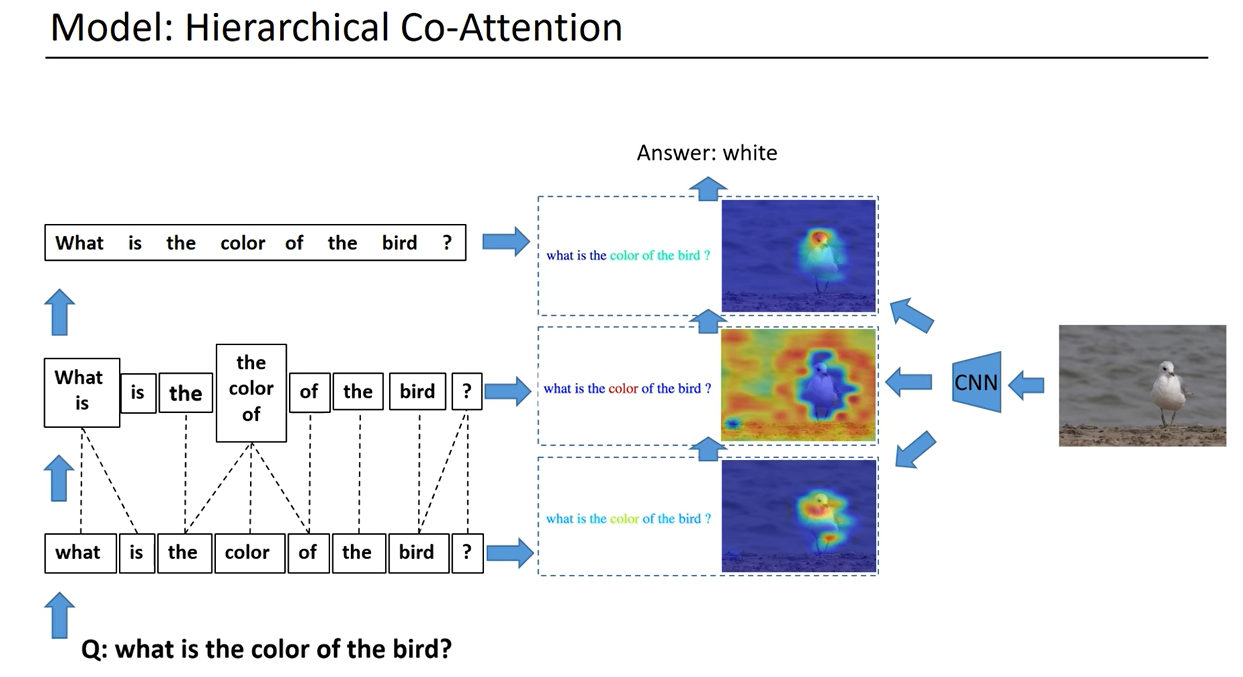
Atthe question level, we use recurrent neural networks to encode the entire question. For each levelof the question representation in this hierarchy, we construct joint question and image co-attentionmaps, which are then combined recursively to ultimately predict a distribution over the answers.
At each level we construct co attention maps that highlight words or phrase in the question as well as regions in the image which are then combined recursively to predict the answer.
The paper proposes two co-attention strategies that differ in the order in which image and question attention maps are generated. The first mechanism, which we call parallel co-attention, generatesimage and question attention simultaneously.